
Period 1
Created by: Clayshia hill
Bacteria Lab
______________________________________________
We are exploring the following claims:
-Bacteria can be found in common places
-Bacteria can have different forms
Background:
-Bacteria is a member of a large group of unicellular microorganisms that have cell walls but lack organelles and an organized nucleus.
-It's life cycle starts in the "lag phase in which bacteria does not grow, but copies DNA. Next, the "log phase" in which bacteria multiply rapidly (binary fission). Then, the stationary phase is when there is a decline in bacteria growth, when growth and death rates are equal. Lastly, the death phase in which bacteria loses its ability to reproduce.
-Bacteria are among the fastest reproducing organisms in the world, doubling every 4 to 20 minutes
-It is a gel-like matrix composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes, and gases and contains cell structures such as ribosomes, a chromosome, and plasmids. The cell envelope encases the cytoplasm and all its components. Unlike the eukaryotic (true) cells, bacteria do not have a membrane enclosed nucleus.
-The major physical factors are pH, temperature, oxygen level, pressure and radiation.
-May 6, 2014 Elizabeth Preston finds that bacteria that have no friends don’t get sad; they get weird. When E. coli cells sense fewer other bacteria around them, their DNA starts to mutate at a faster rate. That’s bad news for humans and our antibiotics. But if we can make bacteria feel less alone, we might be able to slow down their destructive rampages.
-Symbiotic bacteria are bacteria living in symbiosis with another organism or each other. For example, Zoamastogopera, found in the stomach of termites, enable them to digest cellulose.
Make Agar:
Grab an Erlenmeyer flask
Weigh out 2.5g of Agar using the balance. Remember to add agar on the weighing paper first on the balance, then transfer agar to Erlenmeyer flask
Measure out 100ml of H2O from sink, add to flask with Agar powder
Use hot plate to boil agar. DO NOT turn the heat on the highest setting. Stir continuously while stirring, person doing this MUST wear goggles
ONCE BOILING SET A TIMER FOR ONE MINUTE, ONCE ONE MINUTE HASS PASSED, TURN HEAT OFF AND REMOVE FLASK USING TONGS
Let solution cool for 5 minutes, and pour into 3-4 petri dishes
Procedure/Methods Claim #1:
- Take cue tip and a beaker with water
- To collect bacteria at desired location, dip the cue tip in water first, then swab at location being tested
- Gently smear the cotton swab on agar plate in a streaking pattern
- Leave one plate made without adding any bacteria. (Control)
- May do 2 types of bacteria per plate and use sharpie to write underneath where bacteria was collected
- Take a picture of bacteria before putting in incubator
- Place dishes upside down with tape inside the incubator
Gram Staining Claim #2:
-After being inside the incubator for a few days take out petri dishes
-Using a toothpick obtain a small bacteria amount from petri dishes
-Smear the bacteria on 1/2 of the microscopic slide
-Add a small drop of water and mix the bacteria into a smooth mixture
-Air dry slides
-Pass over the flame to heat fix the bacteria
-Add 3 drops of crystal violet so the bacteria is covered
-Rinse gently with water using a pipette
-Hold slide at a 45 degree angle allowing water to flow down the slide
-Add 3 drops of Iodine and allow it to remain on the slide for one minute
-Rinse the slide with water using a pipette
-Add 5 drops of ethyl alcohol and leave on the slide for 5 seconds
-Rinse slide with water using pipette
-Stain with 3 drops of safranin allowing to sit for thirty seconds
-Rinse slide with water using pipette
-Gently blot dry the slide using a paper towel
-Repeat to other bacteria in the other petri dishes
-Observe the slide using the light microscope to identify whether the bacteria is Gram-positive or Gram-negative
Summary:
The research conducted was determining whether bacteria growth is taking place. Our 2 claims were Bacteria can be found in common places and bacteria can have different forms which were both supported by our data. As seen in our experiment we took samples from common plases such as a cell phone, classroom floor, chair seat, etc. and found that there was a lot of bacteria within those places seen in "after" pictures and bacteria can have different forms as seen through the microscope pictures, they can be rod-shaped, spherical, and spiral. Bacteria is very important to life such as Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. These species eat the sugars in milk. As the bacteria eat milk sugars, the bacteria produce lactic acid. Bacteria is also important for cows they have anaerobic bacteria in their digestive tracts which digest cellulose. I have learned that many things contain bacteria such as the human body, which can be in our favor or try to get the human body sick. Bacteria is very unique and without it life could not exist because bacteria helps digest food and is within soil for plants to grow. This lab has shown me that bacteria is everywhere and amazes me how much the human body does to fight bacterial infection due to how much bacteria we encounter on a daily basis.





Before: Control Before: Top - Stair Rail
Bottom - Chair Seat
Before: Top - Phone Before: Top - Door Handle
Bottom - Computer Mouse Bottom - Classroom Floor



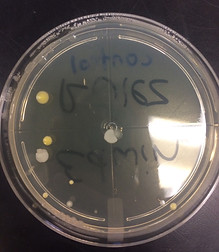
After: Control After: Top - Stair Rail
Bottom - Chair Seat
After: Top - Phone After: Top - Door Handle
Bottom - Computer Mouse Bottom - Classroom Floor



Rod-Shaped Spherical Spiral
(Bacilli) (Cocci)



Phone Classroom Floor
Rod-Shaped Rod-Shaped
Gram-negative Gram-negative
Chair Seat
Spherical
Gram-positive


Data Claim #1 Collected:
Data Claim #2 Collected:
